Arithmetic Sequence 1 1 2 3 5 8

X 6 x 6 1 x 6 2 x 5 x 4 5 3 8.
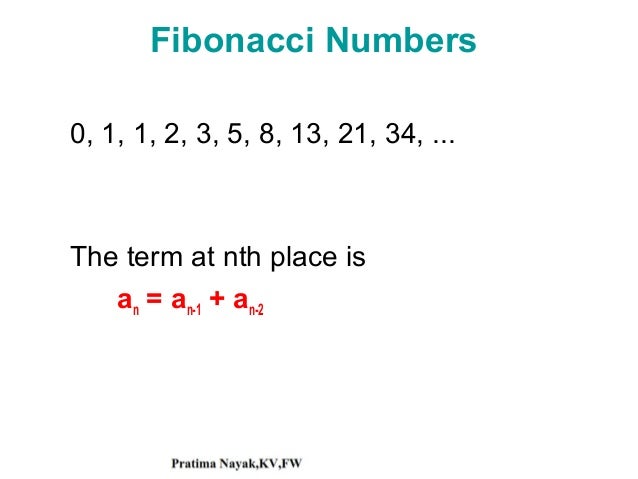
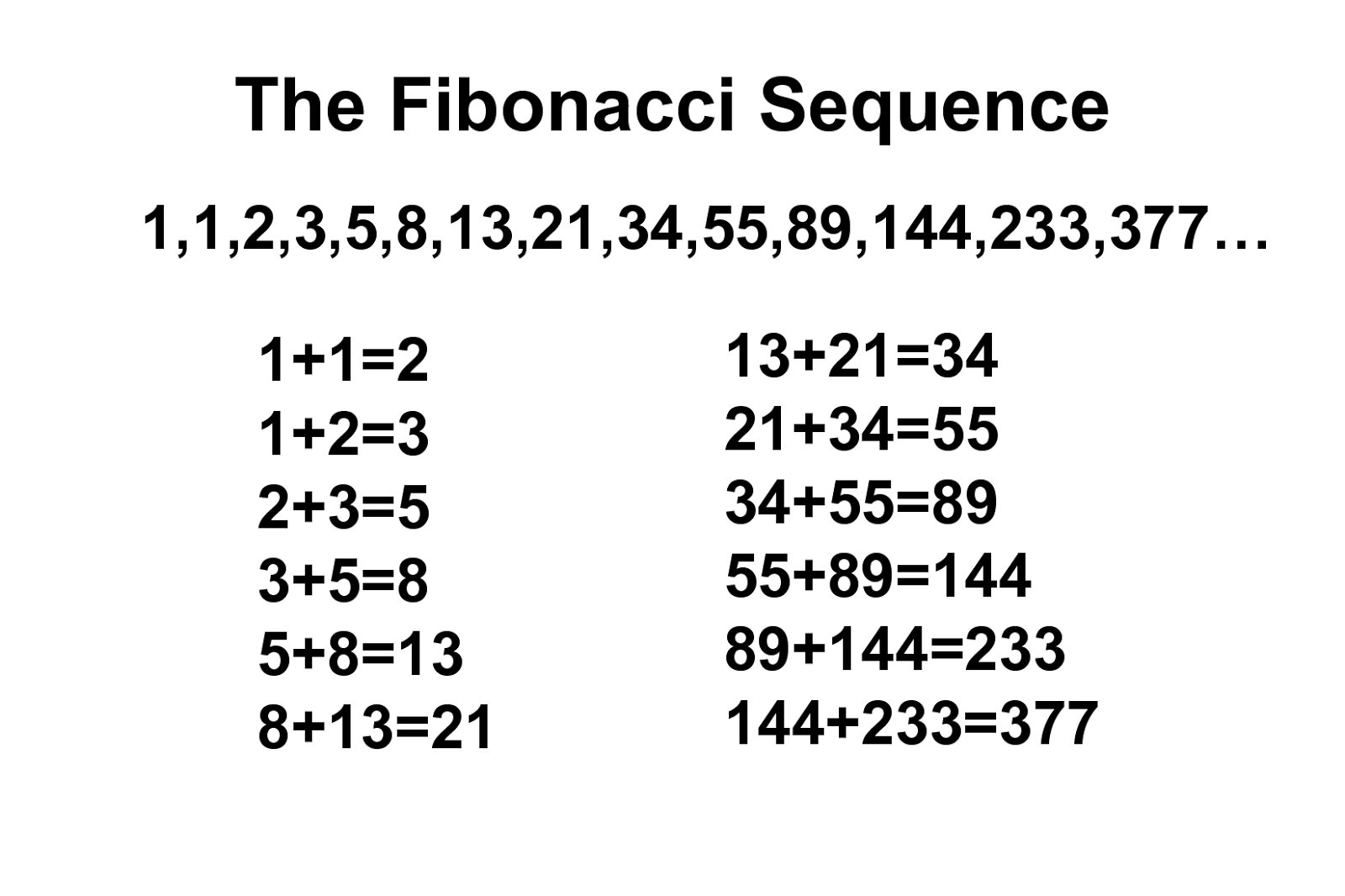
Arithmetic sequence 1 1 2 3 5 8. These are called seed values then the third term is the sum of the previous two terms so a 3 1 1 2. Now you know about sequences the next thing to learn about is how to sum them up. Please enter integer sequence separated by spaces or commas. 1 of 5 you will need.
Write out the sequence. If the initial term of an arithmetic progression is and the common difference of successive members is d then the nth. For example the list of even numbers is an arithmetic sequence because the difference from one number in the list to the next is always 2. 0 1 1 2 3 5 8 13 21 34.
A 5 1 2 5 1 a 5 1 8 9 looking back at the listed sequence it can be seen that the 5th term a 5 found using the equation matches the listed sequence as expected. Look for the common difference and write it down. Series and partial sums. A 1 1 a 2 1 a n a n 1 a n 2 for n 2.
An arithmetic sequence is any list of numbers that differ from one to the next by a constant amount. 1 2 3 4 5. You can also use our above arithmetic sequence formula calculator to make this whole process convenient. Is an arithmetic progression with a common difference of 2.
Then the fourth term is the sum of the second and the third so a 4 1 2 3. That is the first two terms are each defined to have the value of 1. For instance the sequence 5 7 9 11 13 15. If you know you are working with an arithmetic sequence you may be asked to find the very next term from a given list.
So the first term is 1 and the last term is 99. Since 100 is even you would really look at the odd numbers 1 99. In other words we just add some value each time. 3 of 5 step 2.
Find the next number in the sequence using difference table. A 10 2 10 1 2 20 so the 10 th term of this arithmetic sequence would be 20. The fibonacci sequence is the series of numbers. The next number is found by adding up the two numbers before it.
The sequence would be 1 3 5 7 9 etc. 2 of 5 step 1. In an arithmetic sequence the difference between one term and the next is a constant.